If you are an Enterprise user you should consider using the Server-Side Row Model instead of the Infinite Row Model. It offers the same functionality with many more features. The differences between row models can be found in our row models summary page.
Infinite scrolling allows the grid to lazy-load rows from the server depending on what the scroll position is of the grid. In its simplest form, the more the user scrolls down, the more rows get loaded.
The grid will have an 'auto extending' vertical scroll. That means as the scroll reaches the bottom position, the grid will extend the height to allow scrolling even further down, almost making it impossible for the user to reach the bottom. This will stop happening once the grid has extended the scroll to reach the last record in the table.
How it Works
The grid will ask your application, via a datasource, for the rows in blocks. Each block contains a subset of rows of the entire dataset. The following diagram is a high-level overview.
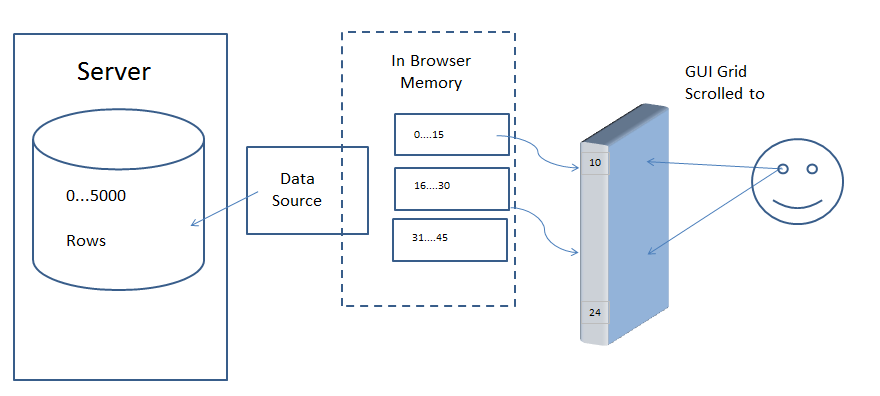
When the grid scrolls to a position where there is no corresponding block of rows loaded, the model uses the provided datasource to get the rows for the requested block. In the diagram, the datasource is getting the rows from a database in a remote server.
Turning On Infinite Scrolling
To turn on infinite scrolling, you must a) set the grid property rowModelType to 'infinite' and b) provide a datasource.
// before grid initialised
gridOptions.rowModelType = 'infinite';
gridOptions.datasource = myDataSource;
// after grid initialised, you can set or change the datasource
api.setGridOption('datasource', myDataSource);
Datasource
A datasource must be provided to do infinite scrolling. You specify the datasource as a grid property or using the grid API.
// set as a property
gridOptions.datasource = myDatasource;
// or use the api after the grid is initialised
api.setGridOption('datasource', myDatasource);
Changing the Datasource
Changing the datasource after the grid is initialised will reset the infinite scrolling in the grid. This is useful if the context of your data changes, i.e. if you want to look at a different set of data.
If you call setGridOption('datasource', datasource) the grid will act assuming it's a new datasource, resetting the block cache. However you can pass in the same datasource instance. So your application, for example, might have one instance of a datasource that is aware of some external context (e.g. the business date selected for a report, or the 'bank ATM instance' data you are connecting to), and when the context changes, you want to reset, but still keep the same datasource instance. In this case, just call setGridOption('datasource', datasource) and pass the same datasource in again.
Datasource Interface
In a nutshell, every time the grid wants more rows, it will call getRows() on the datasource. The datasource responds with the rows requested. Your datasource for infinite scrolling should implement the IDatasource interface:
The getRows() method takes the IGetRowsParams parameters:
getRows()
The getRows() function is called by the grid to load a block of rows into the browser-side cache of blocks. It takes the following as parameters:
The
startRowandendRowdefine the range expected for the call. For example, if thegetRowsfunction is called withstartRow: 0andendRow: 100, then the grid will expect a result with 100 rows (rows 0 to 99).The
successCallback(rowsThisBlock, lastRow)should be called when you successfully receive data from the server. The callback has the following parameters:rowsThisBlockshould be the rows you have received for the current block.lastRowshould be the index of the last row if known.
The
failCallback()should be called if the loading failed. Either one ofsuccessCallback()orfailCallback()should be called exactly once.The
filterModel()andsortModel()are passed for doing server-side sorting and filtering.The context is just passed as is and nothing to do with infinite scrolling. It's there if you need it for providing application state to your datasource.
Setting Last Row Index
The success callback parameter lastRow is used to move the grid out of infinite scrolling. If the last row is known, then this should be the index of the last row. If the last row is unknown, then leave blank (undefined, null or -1). This attribute is only used when in infinite scrolling. Once the total record count is known, the lastRow parameter will be ignored.
Under normal operation, you will return null or undefined for lastRow for every time getRows() is called with the exception of when you get to the last block. For example, if block size is 100 and you have 250 rows, when getRows() is called for the third time, you will return back 50 rows in the result and set rowCount to 250. This will then get the grid to set the scrollbar to fit exactly 250 rows and will not ask for any more blocks.
Block Cache
The grid keeps the blocks in a cache. You have the choice to never expire the blocks, or to set a limit to the number of blocks kept. If you set a limit, then as you scroll down, previous blocks will be discarded and will be loaded again if the user scrolls back up. The maximum blocks to keep in the cache is set using the maxBlocksInCache property.
Block Size
The block size is set using the grid property cacheBlockSize. This is how many rows each block in the cache should contain. Each call to your datasource will be for one block.
Debounce Block Loading
It is also possible to debounce the loading to prevent blocks loading until scrolling has stopped. This can be configured using: blockLoadDebounceMillis.
Aggregation and Grouping
Aggregation and grouping are not available in infinite scrolling. This is because to do so would require the grid knowing the entire dataset, which is not possible when using the Infinite Row Model. If you need aggregation and / or grouping for large datasets, check the Server-Side Row Model for doing aggregations on the server-side.
Sorting & Filtering
The grid cannot do sorting or filtering for you, as it does not have all of the data. Sorting or filtering must be done on the server-side. For this reason, if the sort or filter changes, the grid will use the datasource to get the data again and provide the sort and filter state to you.
Simple Example: No Sorting or Filtering
The example below makes use of infinite scrolling and caching. Notice that the grid will load more data when you bring the scroll all the way to the bottom.
Selection
Selection works on the rows in infinite scrolling by using the Row IDs of the Row Nodes. If you do not provide Keys for the Row Nodes, the index of the Row Node will be used. Using the index of the row breaks down when (server-side) filtering or sorting, as these change the index of the Rows. For this reason, if you do not provide your own Row IDs, then selection is cleared if sort or filter is changed.
To provide your own Row IDs, implement the method getRowId(params), which should return the Key for the data.
gridOptions.getRowId: function(params) {
// the ID can be any string, as long as it's unique within your dataset
return params.data.id.toString();
}
Once you have getRowId() implemented, selection will persist across sorts and filters.
Example: Sorting, Filtering and Selection
The following example extends the example above by adding server-side sorting, filtering and persistent selection.
Any column can be sorted by clicking the header. When this happens, the datasource is called again with the new sort options.
The columns Age, Country and Year can be filtered. When this happens, the datasource is called again with the new filtering options.
When a row is selected, the selection will remain inside the grid, even if the grid gets sorted or filtered. Notice that when the grid loads a selected row (e.g. select first row, scroll down so the first block is removed from cache, then scroll back up again) the row is not highlighted until the row is loaded from the server. This is because the grid is waiting to see what the ID is of the row to be loaded.
The example below uses AG Grid Enterprise, to demonstrate the set filter with server-side filtering. AG Grid Enterprise is not required for infinite scrolling.
When performing multiple row selections using shift-click, it is possible that not all rows are available in memory if the configured value of maxBlocksInCache doesn't cover the range. In this case multiple selections will not be allowed.
Specify Selectable Rows
It is also possible to specify which rows can be selected via the gridOptions.isRowSelectable(node) callback function.
For instance if we only wanted to allow rows where the data.country property is the 'United States' we could implement the following:
gridOptions.isRowSelectable: function(data) {
return data.country === 'United States';
}
Note that in the above example we have also included an optional checkbox to help highlight which rows are selectable.
Configuring a Bit Differently
The examples above use old-style JavaScript objects for the datasource. This example turns things around slightly and creates a datasource Class. The example also just generates data on the fly.
Loading Spinner
The examples on this page use a loading spinner to show if the row is waiting for its data to be loaded. The grid does not provide this, rather it is a simple rendering technique used in the examples. If the data is loading, then the rowNode will have no ID, so if you use the ID as the value, the cell will get refreshed when the ID is set.
loadingSpinnerColumn = {
// use a value getter to have the node ID as this column's value
valueGetter: 'node.id',
// then a custom cellRenderer
cellRenderer: function(params) {
if (params.value === undefined) {
// when no node id, display the spinner image
return '<img src="loading.gif" />';
} else {
// otherwise just display node ID (or whatever you wish for this column)
return params.value;
}
}
}
Refer to section Cell Rendering for how to build cell renderers.
More Control via Properties and API
Infinite scrolling has a cache working behind the scenes. The following properties and API are provided to give you control of the cache.
Properties
API
Adding / removing rows directly in the grid for infinite scrolling is not recommended as it will complicate your application. It will make your life easier if you update the data on the server and refresh the block cache.
Example: Using Cache API Methods
Below demonstrates the different API methods via the buttons. The example outputs a lot of debugging items to the console because the grid property debug=true is set. The buttons are as follows:
- Insert Rows: Inserts 5 rows at row index 2 from the server, then refreshes the grid.
- Delete Rows: Deletes 10 rows at row index 3 from the server, then refreshes the grid.
- Set Row Count: Sets the row count to 200. This adjusts the vertical scroll to show 200 rows. If the scroll is positioned at the end, this results in the grid automatically re-adjusting as it seeks ahead for the next block of data.
- Print Info: Prints
rowCountandmaxFoundto the console. - Jump to 500: Positions the grid so that row 500 is displayed.
- Print Cache State: Debugging method, to see the state of the cache.
- Set Prices High & Set Prices Low: Sets the prices on the server-side to either high or low prices. This will not impact the grid until after a block cache is loaded. Use these buttons to then further test the refresh and purge methods.
- Refresh Cache: Calls for the cache to be refreshed.
- Purge Cache: Calls for the cache to be purged.
The example also makes each Honda row bold - demonstrating that the callbacks getRowStyle and getRowClass get called after the data is set as well as when the row is created (when the data may not yet be available).
Changing Columns
Changing columns is possible using infinite scroll and it does not require the data getting fetched again from the server. If the change of columns impacts the sort or filter (i.e. a column with a sort or filter applied is removed), the grid will fetch data again similar to how data is fetched again after the user changes the sort or filter explicitly.
The example below demonstrates changing columns on the infinite row model. The following can be noted:
- Hit the buttons 'Show Year' and 'Hide Year'. Notice that the data is not re-fetched.
- Add a sort or filter to Age column. When the sort or filter is applied the data is re-fetched. However once fetched, you can add and remove the Year column without re-fetching the data.
- Add a sort or filter to the Year column. When the sort or filter is applied the data is re-fetched. Now remove the Year column and the data is re-fetched again as the sort or filter has changed.
Pagination
As with all row models, it is possible to enable pagination with infinite scrolling. With infinite scrolling, it is possible to mix and match with the configuration to achieve different effects. The following examples are presented:
| Example | Page Size | Block Size | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 | Auto | Large | Most Recommended |
| Example 2 | Equal | Equal | Recommended Sometimes |
Having smaller infinite blocks size than your pagination page size is not supported
You must have infinite block size greater than or equal to the pagination page size. If you have a smaller block size, the grid will not fetch enough rows to display one page. This breaks how infinite scrolling works and is not supported.
Example 1: Auto Pagination Page Size, Large Infinite Block Size
This example is the recommended approach. The infinite block size is larger than the pages size, so the grid loads data for a few pages, allowing the user to hit 'next' a few times before a server sided call is needed.
Example 2: Equal Pagination Page Size and Large Infinite Block Size
This example demonstrates having the page and block sizes equal. Here the server is hit every time a new page is navigated to.
Overlays
The infinite row model does not use overlays like the Client-Side Row Model. It does not use 'loading' overlay as rows load in blocks and it would be wrong to hide all the grid because some rows are getting loaded. The grid does not use 'no rows' overlay as the 'no rows' could be because you have a filter set, and a grid with a filter shows an empty grid when no rows pass the filter.
If you do want to show overlays, then please see overlays section for details on how to show the overlays manually.