This page covers the key concepts of AG Grid: A high performance, feature rich, React Data Table and React Data Grid.
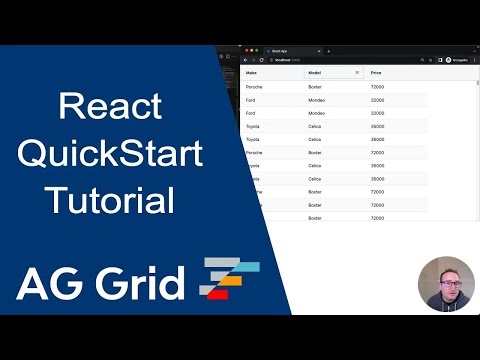
Your First React Grid
Add AG Grid to your application in these steps:
1. NPM Install
npm install ag-grid-react
2. Import the React Grid
import { AgGridReact } from 'ag-grid-react'; // React Data Grid Component
import "ag-grid-community/styles/ag-grid.css"; // Mandatory CSS required by the grid
import "ag-grid-community/styles/ag-theme-quartz.css"; // Optional Theme applied to the grid
3. Define Rows and Columns
const GridExample = () => {
// Row Data: The data to be displayed.
const [rowData, setRowData] = useState([
{ make: "Tesla", model: "Model Y", price: 64950, electric: true },
{ make: "Ford", model: "F-Series", price: 33850, electric: false },
{ make: "Toyota", model: "Corolla", price: 29600, electric: false },
]);
// Column Definitions: Defines the columns to be displayed.
const [colDefs, setColDefs] = useState([
{ field: "make" },
{ field: "model" },
{ field: "price" },
{ field: "electric" }
]);
// ...
}
4. React Grid Component
The AgGridReact component is wrapped in a parent container div. Style is applied to the parent container. Rows and Columns are set as AgGridReact component attributes.
return (
// wrapping container with theme & size
<div
className="ag-theme-quartz" // applying the grid theme
style={{ height: 500 }} // the grid will fill the size of the parent container
>
<AgGridReact
rowData={rowData}
columnDefs={colDefs}
/>
</div>
)
5. Running the React Data Grid
Below is a live example of the application running. Click </> Code to see the code.
To live-edit the code, open the example in CodeSandbox or Plunker using the buttons to the lower-right.
Now that you have a basic React Data Grid running, the remainder of this page explores some of the key concepts.
Showing Data
Mapping Values
The field or valueGetter attributes Map Data to Columns. A field maps to a field in the data. A Value Getter is a function callback that returns the cell value.
The headerName provides the title for the header. If missing the title is derived from field.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{ headerName: "Make & Model", valueGetter: p => p.make + ' ' + p.model},
{ field: "price" },
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />Text Formatting
Format text for cell content using a Value Formatter.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{ field: "price", valueFormatter: p => '£' + p.value.toLocaleString() },
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />Cell Components
Add buttons, checkboxes or images to cells with a Cell Component.
const CustomButtonComponent = (props) => {
return <button onClick={() => window.alert('clicked') }>Push Me!</button>;
};
const [colDefs, setColDefs] = useState([
{ field: "button", cellRenderer: CustomButtonComponent },
// ...
]);
Resizing Columns
Columns are Resized by dragging the Column Header edges. Additionally assign flex values to allow columns to flex to the grid width.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{ field: "make", flex: 2 }, //This column will be twice as wide as the others
{ field: "model", flex: 1 },
{ field: "price", flex: 1 },
{ field: "electric", flex: 1 }
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />Example
This example demonstrates mapping and formatting values, cell components, and resizing columns.
Working with Data
By default, the row data is used to infer the Cell Data Type. The cell data type allows grid features, such as filtering and editing, to work without additional configuration.
Filtering
Column Filters are embedded into each column menu. These are enabled using the filter attribute. The filter type is inferred from the cell data type.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{ field: "make", filter: true },
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />There are 5 Provided Filters which can be set through this attribute. You can also create your own Custom Filter.
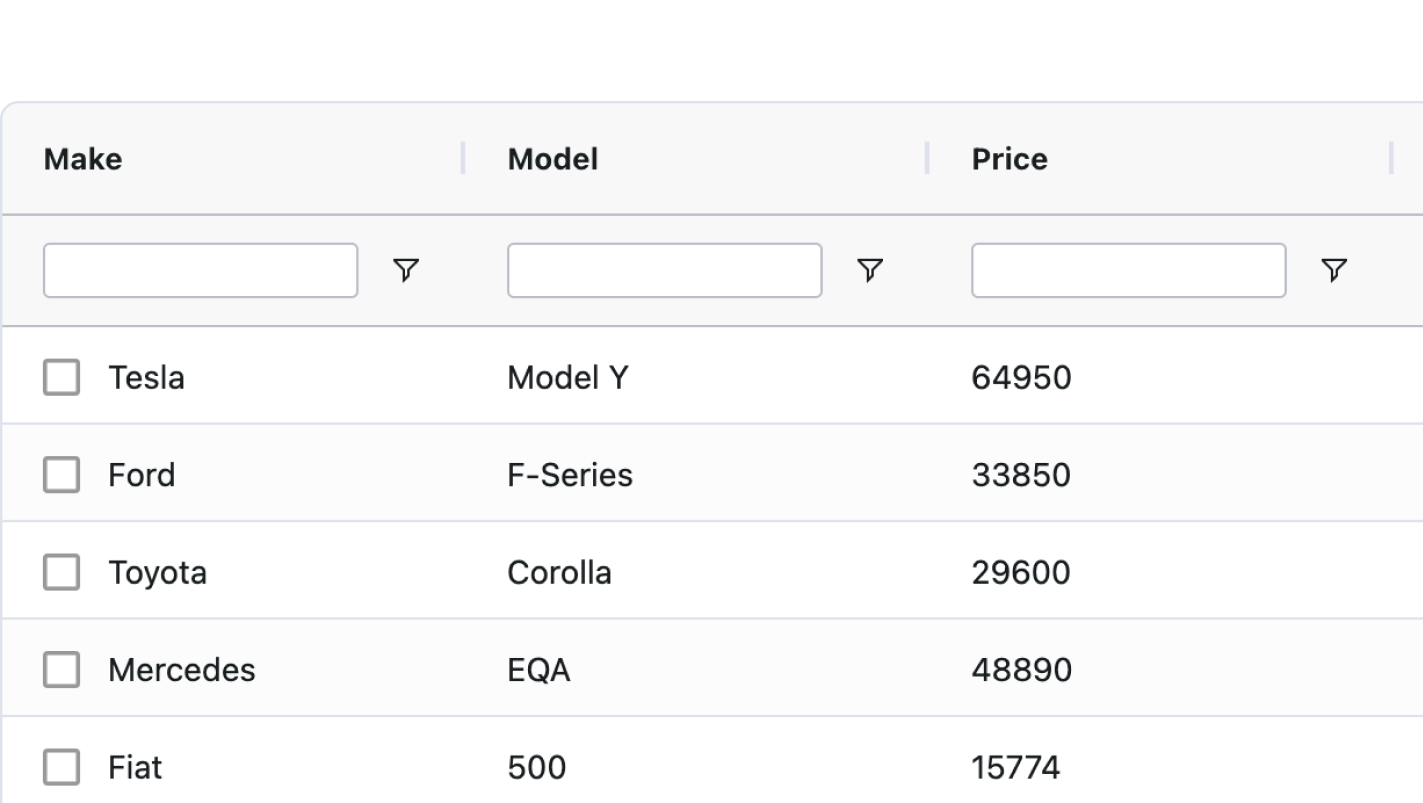
Floating Filters embed the Column Filter into the header for ease of access.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{ field: "make", filter: true, floatingFilter: true },
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />Editing
Enable Editing by setting the editable attribute to true. The cell editor is inferred from the cell data type.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{ field: "make", editable: true },
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />Set the cell editor type using the cellEditor attribute. There are 7 Provided Cell Editors which can be set through this attribute. You can also create your own Custom Editors.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{
field: "make",
editable: true,
cellEditor: 'agSelectCellEditor',
cellEditorParams: {
values: ['Tesla', 'Ford', 'Toyota'],
},
},
]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />Sorting
Data is Sorted by clicking the column headers. Sorting is enabled by default.
Row Selection
Row Selection is enabled using the rowSelection attribute. Use the checkboxSelection column definition attribute to render checkboxes for selection.
// Column Definitions: Defines the columns to be displayed.
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([
{ field: "make", checkboxSelection: true },
]);
const rowSelection = 'multiple';
<AgGridReact
columnDefs={columnDefs}
rowSelection={rowSelection}
/>Pagination
Enable Pagination by setting pagination to be true.
const pagination = true;
const paginationPageSize = 500;
const paginationPageSizeSelector = [200, 500, 1000];
<AgGridReact
pagination={pagination}
paginationPageSize={paginationPageSize}
paginationPageSizeSelector={paginationPageSizeSelector}
/>Example
This example demonstrates filtering, editing, sorting, row selection, and pagination.
Themes & Style
Themes
Grid Themes define how the grid looks (colors, font, spacing etc). The grid comes with Provided Themes such as Quartz and Alpine. To use a theme you need to 1) import the themes CSS and 2) apply the theme to the parent HTML element of the grid.
import "ag-grid-community/styles/ag-theme-quartz.css"; // import Quartz theme
// import "ag-grid-community/styles/ag-theme-alpine.css"; // import Alpine theme, not used here
...
return (
<div class="ag-theme-quartz"> // set Quartz Theme on parent div
<AgGridReact rowData={...} columnDefs={...} />
</div>
)
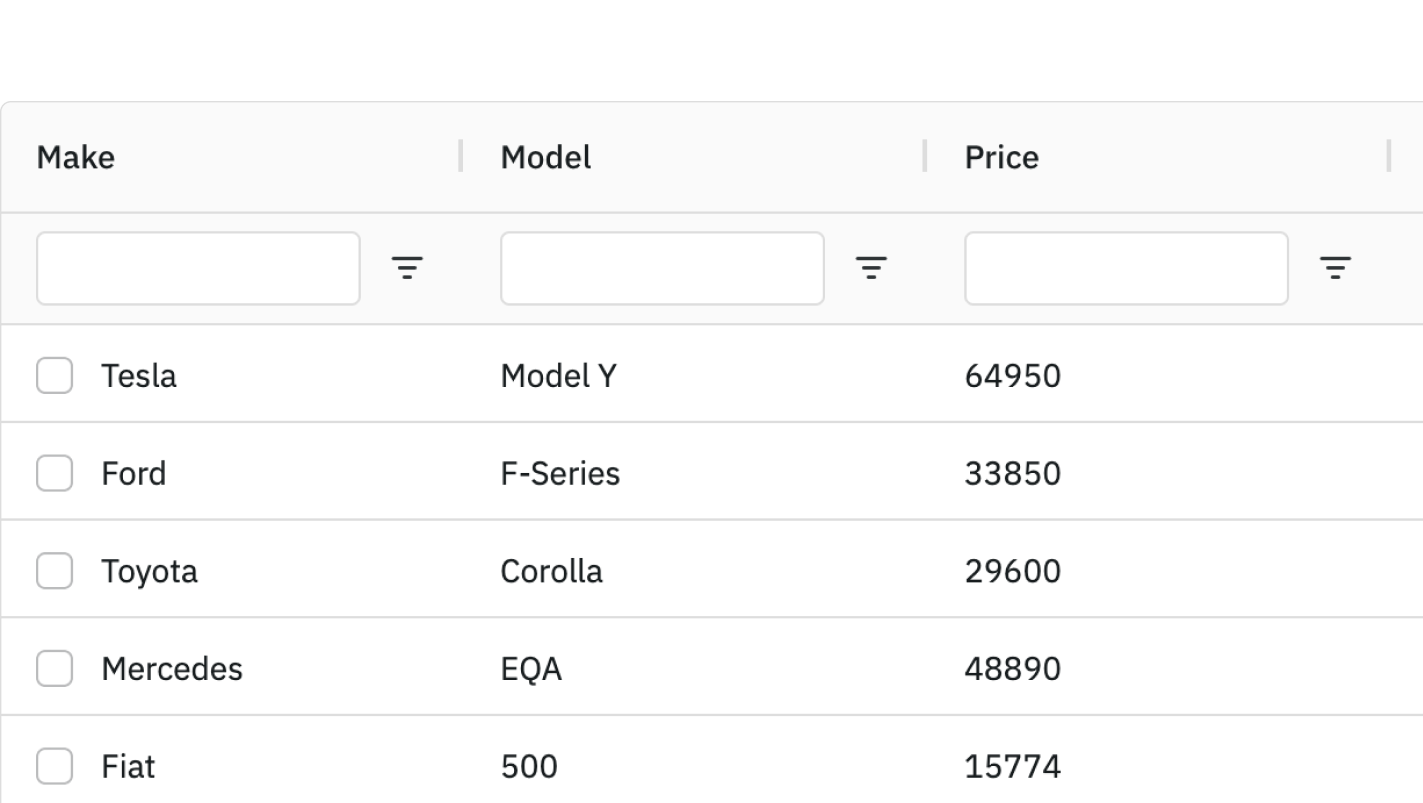
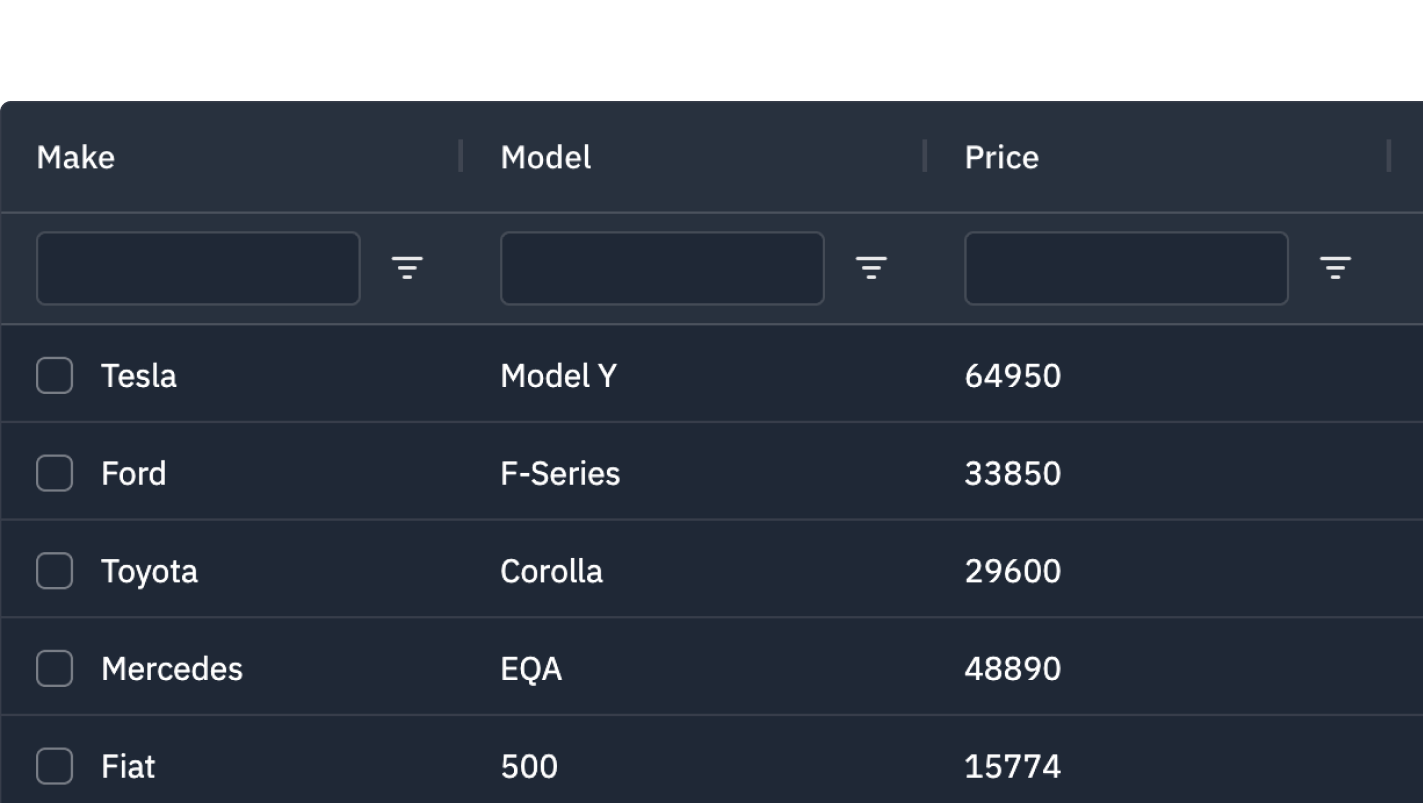
Customising a Theme
Customise Themes using CSS variables.
.ag-theme-quartz {
/* Changes the color of the grid text */
--ag-foreground-color: rgb(14, 68, 145);
/* Changes the color of the grid background */
--ag-background-color: rgb(241, 247, 255);
/* Changes the header color of the top row */
--ag-header-background-color: rgb(228, 237, 250);
/* Changes the hover color of the row*/
--ag-row-hover-color: rgb(216, 226, 255);
}
Figma
If you are designing within Figma, you can use the AG Grid Design System to replicate the Quartz and Alpine AG Grid themes within Figma. These default themes can be extended with Figma variables to match any existing visual design or create entirely new AG Grid themes. These can then be exported and generated into new AG Grid themes.
Cell Style
Define rules to apply Styling to Cells using cellClassRules. This can be used, for example, to set cell background colour based on its value.
.rag-green {
background-color: #33cc3344;
}
const [columnDefs, setColumnDefs] = useState([{
field: 'electric',
cellClassRules: {
// apply green to electric cars
'rag-green': params => params.value === true,
}
}]);
<AgGridReact columnDefs={columnDefs} />Row Style
Define rules to apply Styling to Rows using and rowClassRules. This allows changing style (e.g. row colour) based on row values.
.rag-red {
background-color: #cc222244;
}
const rowClassRules = {
// apply red to Ford cars
'rag-red': params => params.data.make === 'Ford',
};
<AgGridReact rowClassRules={rowClassRules} />Example
This example demonstrates cell style and row style.
Next Steps
- Read our Introductory Tutorial.
- Watch our Video Tutorials.